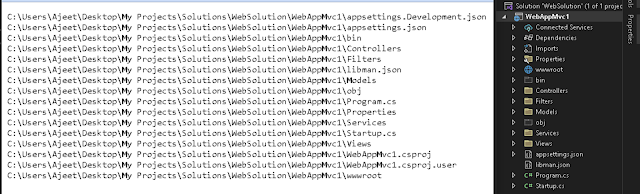
System Namespace types are as follows.
Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders
- IDirectoryContents. Represents a directory's content in the file provider.
- IFileInfo. Represents a file in the given file provider.
- IFileProvider. A read-only file provider abstraction.
- IWebHostEnvironment exposes the app's content root and web root as IFileProvider types.
- Static File Middleware uses File Providers to locate static files.
- Razor uses File Providers to locate pages and views.
- .NET Core tooling uses File Providers and glob patterns to specify which files should be published.
- GetDirectoryContents(String). Enumerate a directory at the given path, if any.
- GetFileInfo(String). Locate a file at the given path.
- Watch(String). Creates a IChangeToken for the specified filter.
- Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.CompositeFileProvider
- Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.EmbeddedFileProvider
- Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.ManifestEmbeddedFileProvider
- Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.NullFileProvider
- Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.PhysicalFileProvider
Example.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
string root = System.IO.Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
IFileProvider fp = new PhysicalFileProvider(root);
services.AddSingleton(fp);
}
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders;
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace WebAppMvc1.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IFileProvider fileProvider;
public HomeController(IFileProvider fileProvider)
{
this.fileProvider = fileProvider;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
var contents = fileProvider.GetDirectoryContents("/");
foreach (var cnt in contents)
{
HttpContext.Response.WriteAsync(cnt.PhysicalPath + Environment.NewLine);
}
return View();
}
}
}
System.IO Namespace
System.IO.Path class
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
private static void Cw(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// path separator character in path string command
Cw(Path.PathSeparator.ToString());
Cw(Path.DirectorySeparatorChar.ToString());
string mypath = @"c:\users\appliedk\abc.pdf";
Cw(Path.GetDirectoryName(mypath));
Cw(Path.GetFileName(mypath));
Cw(Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(mypath));
Cw(Path.GetExtension(mypath));
Cw(Path.GetFullPath("abc.xyz"));
Cw(Path.ChangeExtension(mypath,"docx"));
Cw(Path.EndsInDirectorySeparator(mypath).ToString());
Cw(Path.GetRandomFileName());
Cw(Path.GetTempPath());
Cw(Path.GetTempFileName());
string[] strings = { "abc", "def", "pqr", "xyz" };
Cw(Path.Combine(strings));
Cw(Path.Join(strings));
}
}
}
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting
- IWebHost represents a configured web host. To configuring web host, we use methods of IWebHostBuilder. The IWebHost has methods to start or stop the host. It has Services property that returns IServiceProvider; this interface is implemented by a class or value type that provides a service to other objects because it has GetService(Type) method that returns the service object of the specified type.
- IWebHostBuilder is a builder for IWebHost. It has methods to configure app and services and methods to get the setting value from the configuration or replace a setting in the configuration. It has many extension methods available to do different tasks. They are tabulated below.
- IWebHostEnvironment provides information about the web hosting environment an application is running in. It has two properties. 1) WebRootFileProvider that gets or sets an IFileProvider pointing at WebRootPath. This defaults to referencing files from the 'wwwroot' subfolder and WebRootPath that gets or sets the absolute path to the directory that contains the web-servable application content files. This defaults to the 'wwwroot' subfolder.
- EnvironmentName class has fields for commonly used environment names such as Development, Production etc.
- StartupBase: Base class for initializing services and middlewares used by an application. This class has methods like Configure(IApplicationBuilder): Configures the application. ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection): Register services into the IServiceCollection. CreateServiceProvider(IServiceCollection): Creates an IServiceProvider instance for a given ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection).
- WebHostBuilder class: A builder for IWebHost that implements IWebHostBuilder.
- WebHostDefaults class that contains a set of constants representing configuration keys strings.
|
Build() |
Builds
an IWebHost which hosts a web application. |
|
ConfigureAppConfiguration(Action<WebHostBuilderContext,IConfigurationBuilder>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring the IConfigurationBuilder that will
construct an IConfiguration. |
|
ConfigureServices(Action<IServiceCollection>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring additional services for the host or web application.
This may be called multiple times. |
|
ConfigureServices(Action<WebHostBuilderContext,IServiceCollection>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring additional services for the host or web application.
This may be called multiple times. |
|
GetSetting(String) |
Get the
setting value from the configuration. |
|
UseSetting(String,
String) |
Add or replace
a setting in the configuration. |
|
UseAzureAppServices(IWebHostBuilder) |
Configures
application to use Azure AppServices integration. |
|
CaptureStartupErrors(IWebHostBuilder,
Boolean) |
Set whether
startup errors should be captured in the configuration settings of the web
host. When enabled, startup exceptions will be caught and an error page will
be returned. If disabled, startup exceptions will be propagated. |
|
PreferHostingUrls(IWebHostBuilder,
Boolean) |
Indicate
whether the host should listen on the URLs configured on
the IWebHostBuilder instead of those configured on
the IServer. |
|
Start(IWebHostBuilder,
String[]) |
Start the web
host and listen on the specified urls. |
|
SuppressStatusMessages(IWebHostBuilder,
Boolean) |
Specify if
startup status messages should be suppressed. |
|
UseConfiguration(IWebHostBuilder,
IConfiguration) |
Use the given
configuration settings on the web host. |
|
UseContentRoot(IWebHostBuilder,
String) |
Specify the
content root directory to be used by the web host. |
|
UseEnvironment(IWebHostBuilder,
String) |
Specify the
environment to be used by the web host. |
|
UseServer(IWebHostBuilder,
IServer) |
Specify the
server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseShutdownTimeout(IWebHostBuilder,
TimeSpan) |
Specify the
amount of time to wait for the web host to shutdown. |
|
UseStartup(IWebHostBuilder,
String) |
Specify the
assembly containing the startup type to be used by the web host. |
|
UseUrls(IWebHostBuilder,
String[]) |
Specify the
urls the web host will listen on. |
|
UseWebRoot(IWebHostBuilder,
String) |
Specify the
webroot directory to be used by the web host. |
|
Configure(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<IApplicationBuilder>) |
Specify the
startup method to be used to configure the web application. |
|
Configure(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<WebHostBuilderContext,IApplicationBuilder>) |
Specify the
startup method to be used to configure the web application. |
|
ConfigureAppConfiguration(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<IConfigurationBuilder>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring the IConfigurationBuilder that will
construct an IConfiguration. |
|
ConfigureLogging(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<WebHostBuilderContext,ILoggingBuilder>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring the provided LoggerFactory. This may be called
multiple times. |
|
ConfigureLogging(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<ILoggingBuilder>) |
Adds a
delegate for configuring the provided ILoggingBuilder. This may be
called multiple times. |
|
UseDefaultServiceProvider(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<WebHostBuilderContext,ServiceProviderOptions>) |
Configures the
default service provider |
|
UseDefaultServiceProvider(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<ServiceProviderOptions>) |
Configures the
default service provider |
|
UseStartup(IWebHostBuilder,
Type) |
Specify the
startup type to be used by the web host. |
|
UseStartup<TStartup>(IWebHostBuilder) |
Specify the
startup type to be used by the web host. |
|
UseStartup<TStartup>(IWebHostBuilder,
Func<WebHostBuilderContext,TStartup>) |
Specify a
factory that creates the startup instance to be used by the web host. |
|
UseStaticWebAssets(IWebHostBuilder) |
Configures
the WebRootFileProvider to use static web assets defined by
referenced projects and packages. |
|
UseHttpSys(IWebHostBuilder) |
Specify Http.sys
as the server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseHttpSys(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<HttpSysOptions>) |
Specify
Http.sys as the server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseIIS(IWebHostBuilder) |
Configures the
port and base path the server should listen on when running behind
AspNetCoreModule. The app will also be configured to capture startup errors. |
|
UseIISIntegration(IWebHostBuilder) |
Configures the
port and base path the server should listen on when running behind
AspNetCoreModule. The app will also be configured to capture startup errors. |
|
ConfigureKestrel(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<WebHostBuilderContext,KestrelServerOptions>) |
Configures
Kestrel options but does not register an IServer.
See UseKestrel(IWebHostBuilder). |
|
ConfigureKestrel(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<KestrelServerOptions>) |
Configures
Kestrel options but does not register an IServer.
See UseKestrel(IWebHostBuilder). |
|
UseKestrel(IWebHostBuilder) |
Specify
Kestrel as the server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseKestrel(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<WebHostBuilderContext,KestrelServerOptions>) |
Specify
Kestrel as the server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseKestrel(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<KestrelServerOptions>) |
Specify
Kestrel as the server to be used by the web host. |
|
UseQuic(IWebHostBuilder) |
Specify Quic
as the transport to be used by Kestrel. |
|
UseQuic(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<QuicTransportOptions>) |
Specify Quic
as the transport to be used by Kestrel. |
|
UseSockets(IWebHostBuilder) |
Specify Sockets
as the transport to be used by Kestrel. |
|
UseSockets(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<SocketTransportOptions>) |
Specify
Sockets as the transport to be used by Kestrel. |
|
ConfigureTestContainer<TContainer>(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<TContainer>) |
Configures
the IWebHostBuilder instance with the services provided
in servicesConfiguration. |
|
ConfigureTestServices(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<IServiceCollection>) |
Configures
the IWebHostBuilder instance with the services provided
in servicesConfiguration. |
|
UseSolutionRelativeContentRoot(IWebHostBuilder,
String, String) |
Sets the
content root of relative to the solutionRelativePath. |
|
UseSolutionRelativeContentRoot(IWebHostBuilder,
String, String, String) |
Sets the
content root of relative to the solutionRelativePath. |
|
UseTestServer(IWebHostBuilder) |
Enables
the TestServer service. |
|
UseTestServer(IWebHostBuilder,
Action<TestServerOptions>) |
Enables
the TestServer service. |
System.Environment Class Properties and Methods
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
internal class Program
{
private static void Cw(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Cw(Environment.CommandLine);
Cw(Environment.MachineName);
Cw(Environment.CurrentDirectory);
Cw(Environment.SystemDirectory);
Cw(Environment.UserName);
Cw(Environment.OSVersion.VersionString);
Cw(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop.ToString());
Cw(Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop));
Cw(Environment.ProcessId.ToString());
Cw(Environment.ProcessorCount.ToString());
Cw(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH"));
Cw(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariables().Count.ToString());
Cw(Environment.StackTrace);
}
}
}
Updated on 7 July 2023